Global Health
Zidovudine: how does it work?

More than 60 years have passed for the reason that first detection of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and roughly 40 years since acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) was recognized as a brand new disease. However, we still haven’t got a cure for it. Fortunately, dozens of medication have been developed to treat HIV type 1 (HIV-1), improving the long-term survival of individuals with the disease. The first HIV antiretroviral drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1987 was a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), called zidovudine. Let’s take a take a look at this drug and see how it really works.
HIV life cycle (National Institutes of Health, 2023)
Zidovudine, also generally known as azidothymidine, ZDV, Retrovir, and formerly AZT, is approved for the treatment of HIV-1 infection and the prevention of perinatal transmission of HIV-1 from a pregnant woman to her newborn baby. The drug is not any longer used as monotherapy, but is simplest together with other antiretroviral drugs.
AND
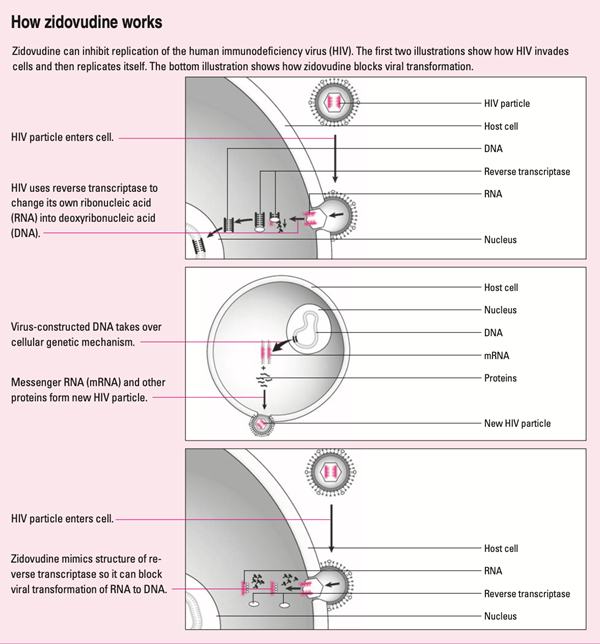
To understand the mechanism of motion of zidovudine, we must always first review the life cycle of HIV. Once HIV enters the body, it attacks CD4, the white blood cells that fight infection.
- HIV first binds to CD4 receptors on the host cell surface.
- HIV and CD4 attach to one another, allowing the virus to enter the CD4 cell.
- Once contained in the CD4 cell, the HIV virus releases and uses the reverse transcriptase enzyme to convert its genetic material, HIV ribonucleic acid (RNA), into HIV deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). This process allows the virus to enter the CD4 nucleus.
- Inside the CD4 nucleus, the HIV virus releases the enzyme integrase, which inserts its DNA into the CD4 cell’s DNA, hijacking the host’s genetic machinery.
- HIV can then use its messenger RNA and host cell CD4 to create long chains of HIV proteins, the constructing blocks of the virus.
- The latest HIV proteins travel to the cell surface and create the immature (non-infectious) HIV virus.
- The latest immature HIV virus pushes itself out of the host’s CD4 cell, releases the enzyme protease, which breaks apart the long protein chains and forms the mature or infectious virus.
How does Zidovudine work?
Zidovudine is an artificial molecule that mimics the structure of reverse transcriptase. It works by integrating with latest viral DNA and inhibiting HIV-1 reverse transcriptase that converts RNA into DNA. This blocks the replication process and disrupts the life cycle of the HIV-1 virus.
Nursing considerations
- Originally developed in oral and intravenous (IV) formulations, the popular route of administration of zidovudine is oral.
- It is not any longer a first-line or monotherapy drug. Zidovudine is run together with other antiretroviral drugs (National Institutes of Health, 2023):
- Abacavir, lamivudine and zidovudine (Trizivir)
- Lamivudine and zidovuding (Combivir)
- Zidovudine is contraindicated in patients who experience a severe, life-threatening allergic response to any component of the drug. It can be contraindicated in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Monitor patients closely for hostile effects including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, myalgia, insomnia, bone marrow suppression, peripheral myopathy, lactic acidosis, elevated liver enzymes, and hepatotoxicity (Edwards, Ingold, & Azmat, 2023) .
- Administration with food may alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Routinely monitor laboratory tests (Facts and Comparisons, 2023):
- Complete blood count (CBC) with differential; assess for signs of hematologic toxicity, bone marrow suppression, neutropenia, leukopenia, and anemia.
- Liver function tests (LFT); zidovudine has been related to severe hepatomegaly with steatosis.
- serum creatinine; assess for signs of renal impairment; the dose may should be adjusted.
- HIV viral load
- CD4 count
Regardless of the antiretroviral regimen chosen, patient education is of the utmost importance. Emphasize that adherence to treatment will improve the patient’s quality of life, reduce the danger of infection or cancer, and extend overall survival (Edwards, Ingold, & Azmat, 2023).
AND
Full details may be present in the leaflet that comes with the medication or within the Nursing2024 Medicines Manual + medicines updates.
AND
AND
Edwards, Z., Ingold, C. J., & Azmat, C. E. (2023, February 11). Zidovudine. StatPearls [Internet] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554419/
AND
Facts and Comparisons (2023, July 31). Zidovudine orally. Facts and comparisons. https://fco.factsandcomparisons.com/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/fc_dfc/5549800
AND
National Institute of Health. (2023, March 23). FDA-approved HIV drugs. https://hivinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv/fact-sheets/fda-approved-hiv-medicines.
AND
AND
-

 Well-Being1 year ago
Well-Being1 year ago5 books that may help at work at work
-

 Global Health1 year ago
Global Health1 year agoThe Global Fund opens up the potential of private sector investment – updates
-

 Well-Being1 year ago
Well-Being1 year agoFast and healthy advice on preparing meals for busy nurses
-

 Well-Being12 months ago
Well-Being12 months agoMaintenance of the nursing engine – each day nurse
-

 Best Practice11 months ago
Best Practice11 months agoSafety within the workplace as an ethical imperative in nursing
-

 Best Practice1 year ago
Best Practice1 year agoA cultural approach to the treatment of neonatal pain
-
 Well-Being1 year ago
Well-Being1 year agoHow to get the standard of sleep for higher mental health
-

 Education12 months ago
Education12 months agoAI for teachers – Nursing Education Network






